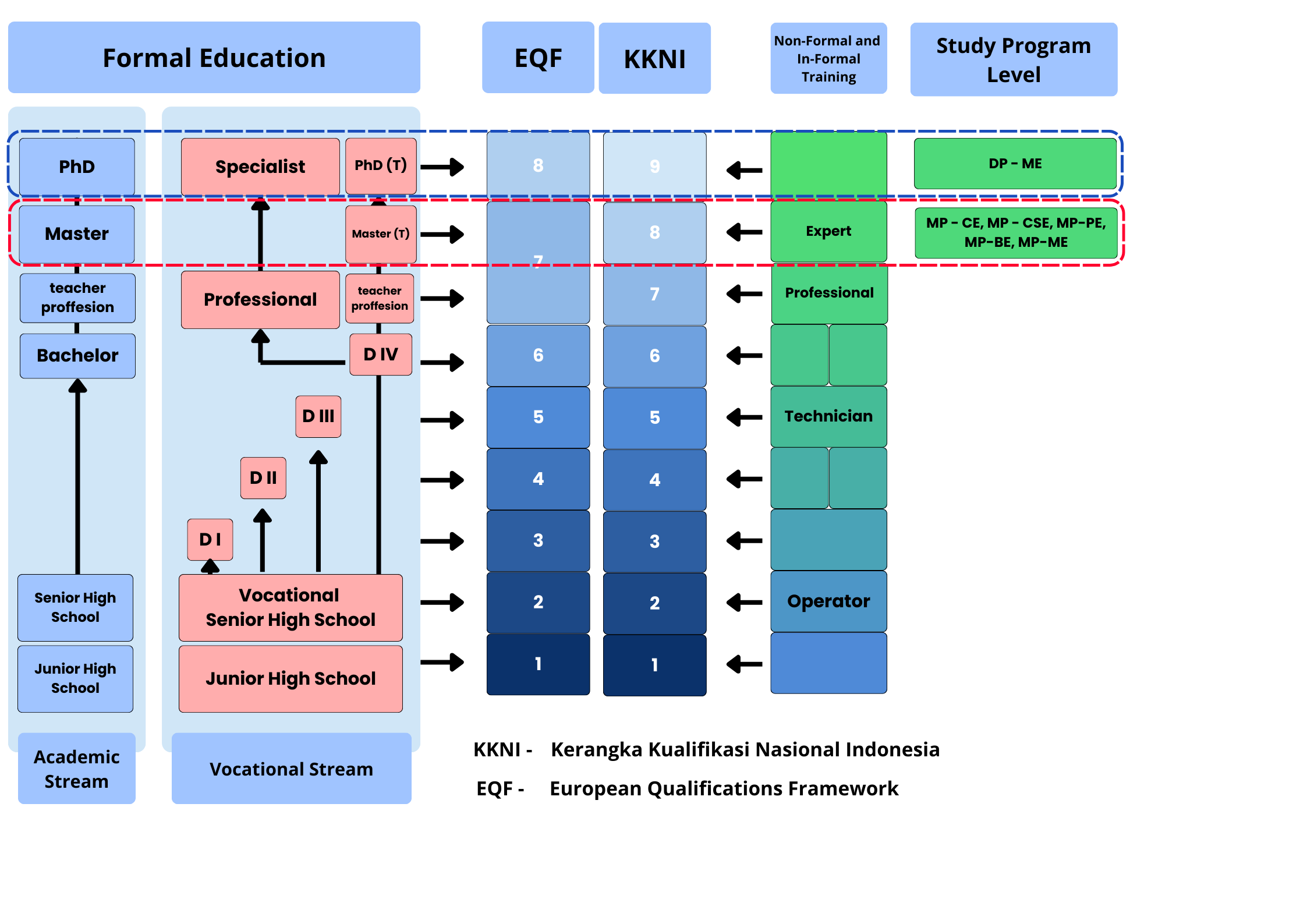
The curriculum of UPI's study programs align with the KKNI, incorporating 21st-century skills and Industrial Revolution 4.0 demands. This alignment ensures the curriculum meets graduate competency standards while addressing workforce needs. At EQF level 7 and KKNI level 8, qualifications reflect the competencies expected of Master’s level graduates. MP-CSE is designed to produce experts capable of integrating theory and practice, conducting scientific research, and offering knowledge-based solutions to complex problems. Critical thinking, creativity, and leadership are key competencies emphasized at this level. As shown in Figure below, KKNI level 8 is applied to Master’s programs, and level 9 to Doctoral programs.
Currently, two curricula are in use: Curriculum 2018 and Curriculum 2023, which are evaluated continuously and refined to adapt to changing needs:
- Objectives
- Degree of study program
- Curriculum Development Study
- Graduate Qualification Profile
- Learning Outcomes
- Curriculum structure
- List and distribution of courses
- Learning process
- Assessment
- Mapping PLO versus Qualification Profile
- Mapping PLO versus Courses
- Objectives
- Degree of study program
- Curriculum Development Study
- Graduate Qualification Profile
- Learning Outcomes
- Curriculum structure
- List and distribution of courses
- Learning process
- Assessment
- Mapping PLO versus Qualification Profile
- Mapping PLO versus Courses
Curriculum 2018
1. Objectives
Referring to the vision and mission, the following are the objectives of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program:
- To produce graduates who are faithful and devoted to God Almighty, manifested by an attitude of integrity, honesty, empathy, and responsibility.
- To produce graduates who are able to apply the noble values of Pancasila and have a high sense of nationalism.
- To produce graduates who have competence in theories/concepts and implementations in the fields of education, software engineering, multimedia, computer networks, and other latest technologies.
- Produce graduates who are able to carry out research independently to solve problems in the world of education by involving various disciplines.
- Produce graduates as experts in the field of computer science education who are ready to enter and work in Indonesian and international communities.
- Produce graduates who have the ability to build networks/cooperation, communication, and high self-development.
2. Degree of study program
The degree for graduates of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program is “M.Pd.”
3. Curriculum Development Study
The industrial revolution 4.0 brought many changes, especially in the industrial sector involving digitalization from all walks of life. This began with the use of the internet that connected various tools, which became known as the Internet of Things. So, each of these tools can communicate, exchange data, and with programmed artificial intelligence methods, the tool can finally make decisions based on the input data received from various available sensors. Computer programs embedded in tools can involve various concepts and technologies in artificial intelligence, including Machine Learning. With this machine learning, the algorithm has the ability to learn automatically from the incoming training data. This computing process can also involve Cloud Computing technology, so that the data and knowledge used can be stored on the internet network provided by the Cloud Computing vendor. That way, various reliable and safe services can be obtained and used at any time and place.
The industrial revolution 4.0 cannot be utilized by the Indonesian people without education that is able to adopt and rely on progress and changes in this revolution. To achieve this, education must have learning methods, curricula, and other tools that: (i) support the improvement of critical thinking skills, (ii) have creativity and innovative abilities, (iii) have good communication skills and abilities, (iv) have the ability to cooperate and work in teams, and (v) have high flexibility and adaptability to be able to keep up with rapid technological developments. This is in line with various current educational concepts, which are better known as “Education for the 21st Century” (or education for the 21st century). This education is simply a learning that provides 21st century skills to students to be able to communicate, collaborate, think critically and solve problems, be creative and innovative, and master information technology. For this reason, the application of a scientific approach is needed to achieve the target of this student's ability.
On the other hand, with the development of technology and the need for the abilities of students in the 21st century, teachers/teachers also need to prepare themselves so that they are able to meet various competency requirements to carry out their duties and authorities professionally in accordance with existing demands and regulations. Various opinions explain that the challenges of teachers in the 21st century are not simple, namely:
- Teaching in multicultural society: Teachers need to be able to teach in a society that has cultural and linguistic differences.
- Teaching for the construction of meaning: Teachers must have the ability to construct a concept.
- Teaching for active learning: Teachers can apply active learning methods for their students.
- Teaching with technology: Teachers are able to involve the latest technology in their teaching.
- Teaching that focuses on carácter building: Teachers do not teach knowledge, but are also tasked with building good character for their students.
- Teaching for the hard and soft skills: Teachers are tasked with building skills in terms of knowledge, creativity, communication, and solving a problem to improve student competitiveness.
Therefore, in line with the changing phenomena and challenges that have been described previously, the Department of Computer Science Education responded by opening a Masters Program in Computer Science Education. This study program is designed in 38 credits which contains teaching and strengthening materials in the fields of education, computer network technology, multimedia technology, software engineering, and other capabilities that are in line with current trends (among others artificial intelligence/machine learning, digital pedagogy, data analysis, internet of things, etc.). So, briefly, this master's study program is expected to be able to provide solutions to the challenges that must be faced by teachers, especially teachers in the field of computer science.Therefore, in line with the changing phenomena and challenges that have been described previously, the Department of Computer Science Education responded by opening a Masters Program in Computer Science Education. This study program is designed in 38 credits which contains teaching and strengthening materials in the fields of education, computer network technology, multimedia technology, software engineering, and other capabilities that are in line with current trends (among others artificial intelligence/machine learning, digital pedagogy, data analysis, internet of things, etc.). So, briefly, this master's study program is expected to be able to provide solutions to the challenges that must be faced by teachers, especially teachers in the field of computer science.
3.1 Comparative Analysis of Computer Science Education Master's Programs at Ex-LPTK Universities
In this subchapter, the results of a survey on master's degree programs in computer science education or the like at several universities will be reviewed, which is a change/replacement from the state Education Personnel Education Institution (LPTK). As information is available on the official website of LPTK universities, it can be seen that:
-
Universitas Negeri Padang (UNP, http://pps.unp.ac.id/ ): There are 3 master programs, namely Educational Technology, Environmental Science, and Social Studies Education. Of the three Study Programs, the one that has similarities with Computer Science Education is the Education Technology Study Program. Based on the curriculum offered in this study program, we can see that the focus of the study program's expertise is on technology related to improving teaching, such as multimedia, web-based learning, and distance learning technology. So it can be said that this study program does not provide sufficient lecture material to improve professional skills and knowledge of computer science or informatics. On the other hand, the proposed Masters Program in Computer Science Education at the Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia does not only focus on improving the ability of teachers on teaching and educational models/methods but also on the professions in the field of computer science, namely multimedia, software engineering, computer networks, and technology. latest in computer science.
-
Universitas Negeri Semarang (UNNES, http://pps.unnes.ac.id/): Based on the information presented on the website, there are 21 master study programs. However, there is no study program related to computer science and informatics or anything similar to this.
-
Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta (UNY, http://pps.uny.ac.id/ ): Based on the information on the website, there are more than 10 master programs. From the study program, the master study program that is similar to this proposal is the master program for electronics and informatics engineering education. Based on the curriculum in this study program, there are several basic courses taught, namely computer networks, information systems, and vocational learning models. So overall, the evaluation of the Study Program curriculum is more repeating the courses that have been taught at the undergraduate level and less adopting the latest technological developments. This is different from this proposed Masters Study Program which has proposed for a more in-depth and comprehensive course than at the undergraduate level and has adopted current technological developments.
- Universitas Negeri Malang (UM, http://pasca.um.ac.id/ ): At UM postgraduate there are more than 30 Masters Study Programs. However, none of the Masters Study Programs is the same and similar to the Masters Program in Computer Science Education as proposed in this proposal.
-
Universitas Negeri Jakarta (UNJ, http://pps.unj.ac.id/ ): Several Masters Programs are offered by the Postgraduate UNJ, one of which is the Masters Program in Educational Technology. As stated in the curriculum in this study program, the focus of education is on preparing teachers to be experts in building learning media and technology. So, it can be said that there is no Master Study Program that is the same/similar to the proposal in this proposal.
-
Universitas Negeri Surabaya (UNESA, https://pasca.unesa.ac.id/ ): Of the Masters Programs offered by UNESA, there is no study program that has similarities to Computer Science Education or Information Technology Education.
From the surveys mentioned above, it can be concluded that the Master Program in Computer Science Education can fill the void in fulfilling and improving the teaching profession in the field of computer science/informatics. Furthermore, the establishment of the Master Program in Computer Science Education for the first time at the LPTK University can strengthen the motto of the Indonesian Education University, which is "Leading and Outstanding".
3.2 Analysis of Computer Science Expertise Based on Professional Institutions
In the field of Computer Science, there are 2 overseas professional institutions that have become references by universities around the world, namely the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). These two professional institutions have compiled a Computing Curricula which is a guide in the preparation of the curriculum (especially for the undergraduate level) in the field of computing. Briefly, the expertise group in computing can be divided into 6 fields, namely Electrical Engineering (EE), Computer Engineering (CE), Computer Science (CS), Software Engineering (SE), Information Technology (IT), and Information Systems (IS). From the six fields, it is clear that the Master Program in Computer Science Education proposed in this proposal is closely related to the field of Computer Science (CS).
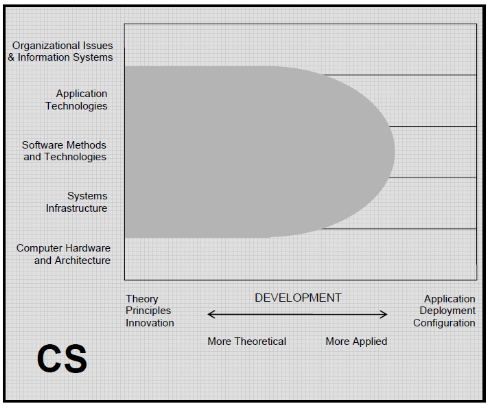
Based on the Computing Curricula compiled by IEEE and ACM, CS focuses on theory and algorithmic foundations for technology development such as robotics, computer vision, intelligent systems, bioinformatics, and others. CS also focuses on techniques to design, implement, and find effective ways to solve computational problems, as illustrated in the figure below:
It is clear that computer science includes innovations in theory and principles with a wide range of applications. Application technologies, software methods and technologies and system infrastructure are also discussed in this field. However, computer science has very little to say about organizational issues and computer hardware and architecture. From this aspect, it is then revealed to be the main subject that must be taught in computer science. These courses include algorithm and programming fundamentals, operating system design and principles, programming language theory, intelligent systems, scientific computing, and software design.
In the field of computer science education, there is also a professional institution for computer science teachers in America, namely the Computer Science and Teachers Association (CSTA). CSTA formulates 9 policies as the basis for computer science education at the secondary and high school levels, as illustrated in the figure below.
4. Graduate qualification profile
Graduates of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program have general graduate competencies which include aspects of attitudes and values. In addition, graduates of computer science education also have special competencies that must be mastered by graduates which include knowledge, general skills and special skills. Thus, the profile of graduates of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program can be seen as follows:
- Educator: Graduates who have the competence to educate, teach, guide, direct, train, assess, evaluate, and develop education and learning.
- Professional: Graduates who work in the industrial world who require special skills in the fields of computer science (programmers, multimedia designers, and networking engineers) and education.
- Technopreneur: Graduates who work independently by utilizing knowledge in the fields of education and computer science.
- Advanced Study: Graduates who continue to a higher level study, namely Doctoral.
5. Learning Outcomes
The following are the Learning Outcomes of Master of Computer Science Education:
6. Curriculum structure
The curriculum structure of the Computer Science Education master's program is designed to 4 semesters with a total of 38 credits, consisting of 7 credits of Postgraduate Expertise Courses (MKKPs), 17 credits of core expertise courses (MKKP), 6 credits of elective courses Study Program, and 8 Thesis Credits. Distribution per semester can be seen in the table below:
| Semester | Credit |
| Semester I | 12 Credits |
| Semester II | 12 Credits |
| Semester III | 6 Credits |
| Semester IV | 8 Credits |
| Total Credits | 38 |
Figure below illustrates the curriculum structure across four semesters, totaling 75 ECTS, offering a comprehensive overview of the program's academic framework.
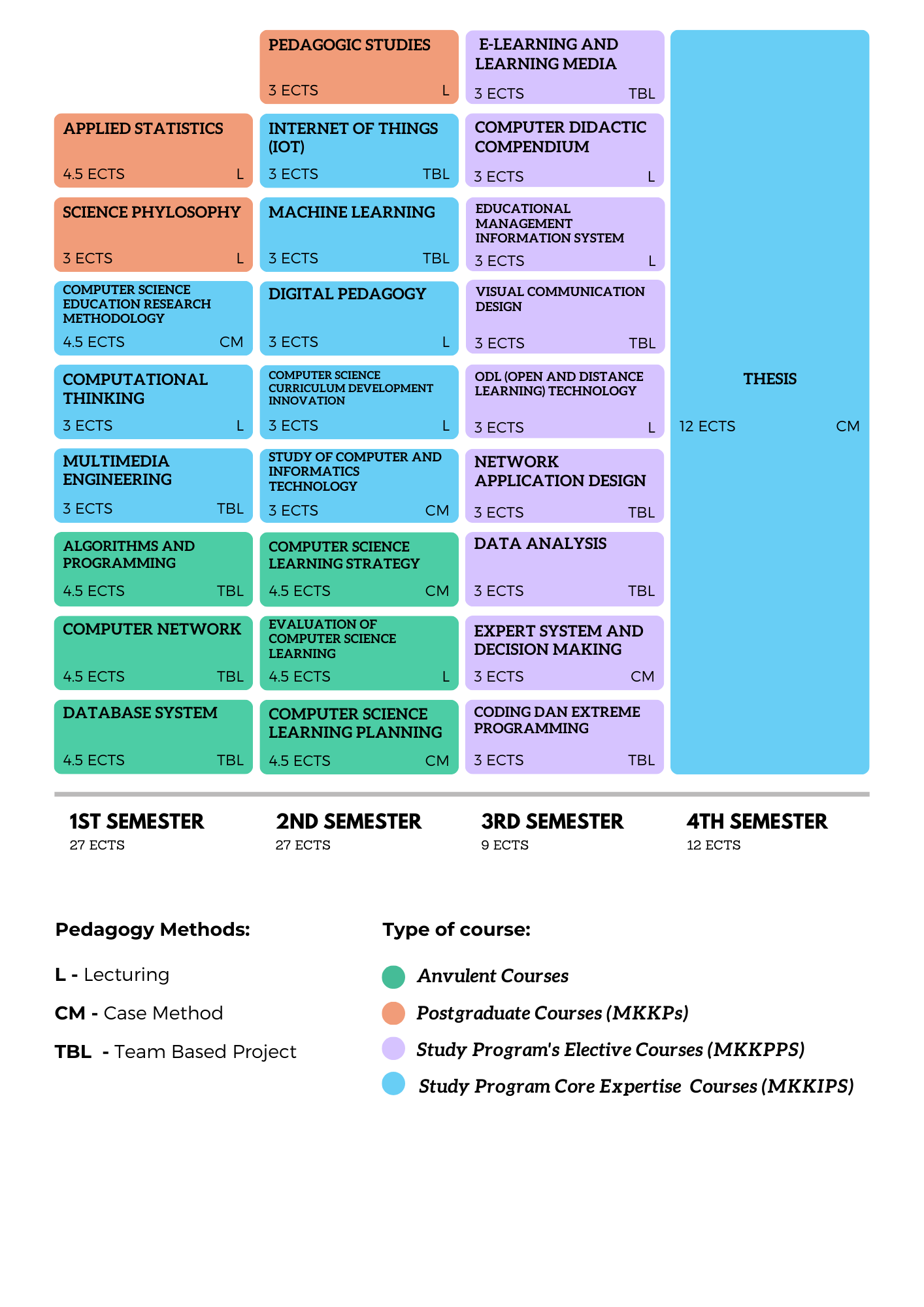
7. List and distribution of courses
The following table is a complete list of courses in the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program:
A. Postgraduate Courses (MKKPs)
| NO | CODE |
|
|
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| 1 | PS701 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 2 | PS702 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 3 | PS703 |
|
X | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
B. Study Program Core Expertise Courses (MKKIPS)
| NO | CODE |
|
|
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| 1 | IK700 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 2 | IK710 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 3 | IK720 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 4 | IK730 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 5 | IK740 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 6 | IK750 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 7 | IK760 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 8 | IK770 |
|
X | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
C. Study Program's Elective Courses (MKKPPS)
| NO | CODE |
|
|
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| 1 | IK711 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 2 | IK721 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 3 | IK731 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 4 | IK741 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 5 | IK712 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 6 | IK722 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 7 | IK732 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 8 | IK742 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 9 | IK752 |
|
X | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
| NO | CODE |
|
|
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| 1 | IK798 |
|
X | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Matriculation Course (AANVULLEN)
| NO | CODE |
|
|
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||
| 1 | IK131 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 2 | IK213 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 3 | IK211 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 4 | IK404 | Computer Science Learning Strategy |
|
X | |||||||
| 5 | IK401 |
|
X | ||||||||
| 6 | IK402 | Computer Science Learning Planning |
|
X | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
8. Learning Process
The learning process is designed so that it has the characteristics, planning and implementation of a good learning process and has a well-distributed learning load. The characteristics of the learning process are interactive, holistic, integrative, scientific, contextual, thematic, effective, collaborative, and student-centered. The characteristics of this process are outlined in learning outcomes that reflect the learning process that encourages the formation of a comprehensive and broad mindset by internalizing local and national excellence and wisdom. The existence of linkages between learning outcomes with each other requires the learning process to be developed thematically, integratively, collaboratively, and contextually in accordance with the demands of the ability to solve problems in the scientific realm of computer science education, with a scientific approach so as to create an academic atmosphere that forms values in accordance with the norms, religion and national ethics. The learning process can be carried out in various forms such as lectures, responses, tutorials, seminars, practicums, field practices, and or through school field introduction programs. Learning methods adapt to developments and needs through interactions between lecturers, students and learning resources in schools, industry and other environments that are considered effective in achieving learning outcomes.
9. Assessment
Assessment using a standard bias as guidance in assessing the learning process and results in order to achieve the learning outcomes. The principle of assessment refers to learning assessment standards which include educative, authentic, objective, accountable, and transparent principles which are carried out in an integrated manner. The assessment techniques used include written tests, practical tests as well as performance and/or products as student work in the form of comprehensive assignments. Attitude assessment is carried out throughout learning through moral messages and directions related to learning activities, either directly or indirectly and set forth in the appropriate rubric form, while for the assessment of knowledge and skills using one or a combination of the assessment techniques that have been mentioned.
The end result of learning is the integration of established assessment techniques and instruments by upholding the principle of transparency. The mechanism for implementing the assessment is carried out starting from the preparation, implementation, providing feedback, as well as publication and documentation in accordance with the schedule set by the university. Furthermore, the assessment of learning achievement every semester is poured with a semester achievement index.
10. Mapping PLO versus Qualification Profile
| Learning Outcome Code | Program Learning Outcome | GRADUATE PROFILE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Educator | Professional | Technopreneur | Further Study | ||
| PLO-1 | Must be able to demonstrate scientific, educational, and religious attitudes and behaviors that contribute to improving the quality of life in society, at the national, and state levels, based on cultural ethics, norms, and academic standards. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| PLO-2 | Must be able to integrate learning and innovation skills, mastery of technology and information, career development, and life skills to become lifelong learners. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| PLO-3 | Must be able to develop and publish logical, critical, systematic, and creative thinking through scientific research, design creation, or artistic works with interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approaches while considering and applying humanitarian values in their fields of expertise. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| PLO-4 | Must be able to develop and apply knowledge in computer science education with a focus on ethics and humanity, solve interdisciplinary problems, conduct and publish research for the benefit of society, and build networks within the education and research communities. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| PLO-5 | Must be able to focus on mastery of scientific principles in computing, education, and research methodologies to enhance learning, solve computational problems, and produce innovative works that have an impact on computer science education. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| PLO-6 | Must be able to advance knowledge and technology in education and software engineering through creative and innovative interdisciplinary research to achieve outcomes that are effective, efficient, and responsive to societal needs. | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| PLO-7 | Must be able to emphasize the importance of creative and innovative research in design, multimedia, computer networks, and emerging fields (such as AI, IoT, and 21st-century education) to meet societal needs and achieve effective, efficient, and reliable results. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
11. Mapping PLO versus Courses
| No | Code | Course Title | Credits | PLO-1 | PLO-2 | PLO-3 | PLO-4 | PLO-5 | PLO-6 | PLO-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PS701 | Applied Statistics | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 2 | PS702 | Science Philosophy | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 3 | PS703 | Pedagogic Studies | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Total Credits | 7 | |||||||||
| No | Code | Course Title | Credits | PLO-1 | PLO-2 | PLO-3 | PLO-4 | PLO-5 | PLO-6 | PLO-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IK700 | Computer Science Education Research Methodology | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 2 | IK710 | Computational Thinking | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 3 | IK720 | Multimedia Engineering | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 4 | IK730 | Internet of Things (IoT) | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 5 | IK740 | Machine Learning | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 6 | IK750 | Digital Pedagogy | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 7 | IK760 | Computer Science Curriculum Development Innovation | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 8 | IK770 | Study of Computer and Informatics Technology | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Total Credits | 17 | |||||||||
| No | Code | Course Title | Credits | PLO-1 | PLO-2 | PLO-3 | PLO-4 | PLO-5 | PLO-6 | PLO-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IK711 | E-learning and Learning Media | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 2 | IK712 | ODL Technology | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 3 | IK721 | Computer Didactic Compendium | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 4 | IK722 | Network Application Design | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 5 | IK731 | Educational Management Information System | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 6 | IK732 | Data Analysis | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 7 | IK741 | Visual Communication Design | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 8 | IK742 | Expert System and Decision Making | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 9 | IK752 | Coding dan Extreme Programming | 2 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 10 | IK798 | Tesis | 8 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Total Credits | 26 | |||||||||
| No | Code | Course Title | Credits | PLO-1 | PLO-2 | PLO-3 | PLO-4 | PLO-5 | PLO-6 | PLO-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IK131 | Algorithms and Programming | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 2 | IK211 | Database System | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 3 | IK213 | Computer Network | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 4 | IK401 | Evaluation of CS Learning | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 5 | IK402 | CS Learning Planning | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| 6 | IK404 | CS Learning Strategy | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | |||||
| Total Credits | 18 | |||||||||
Curriculum 2023
1. Objectives
Referring to the vision and mission, the following are the objectives of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program:
- To produce graduates who have faith and devotion to God Almighty, manifested by integrity, honesty, empathy, and responsibility.
- To produce graduates who apply Pancasila's values and have a strong sense of nationalism.
- To master the theory and implementation of education, software engineering, multimedia, and computer networks.
- To conduct independent research solving educational problems with interdisciplinary approaches.
- To develop experts in computer science education for both national and international settings.
2. Degree of Study Program
The degree awarded to graduates of the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program is "M.Pd."
3. Curriculum Development Study
Evaluation of the curriculum program is carried out to assess the suitability of the curriculum design developed and how the implementation of the curriculum is towards the profile of the graduates produced. In formulating the curriculum, the MP-CSE has developed a Curriculum Development Team (TPK). In the process, the curriculum development team uses various data as input from curriculum design, including tracer study data and the results of user needs analysis. In addition, the learning outcomes compiled are ensured to be in accordance with KKNI competencies at level 8.
Each learning outcome that is compiled can be mapped well to the courses of the Computer Science Education Study Program. In its implementation, to achieve these learning outcomes, each course has complete RPS details that describe how the CP can be achieved. In addition, a lecture contract is prepared to ensure the continuity of achieving the CP of each course. Each student, assisted by the Academic Advisor lecturer, must follow the lecture contract with a predetermined scheme. The output of the study program curriculum is alumni who have graduated.
In addition, the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program also considers various external conditions, namely as follows:
- Advances in information and communication technology: Currently, advances in information and communication technology have affected the joints of our lives, both political, economic, policy, social, educational, and cultural aspects. This is reinforced by the Covid-19 pandemic, which requires us to maintain distance or reduce direct/face-to-face interactions. Thus, the implementation of online and blended learning becomes urgent. Digital technology for online and blended learning can use Learning Management System (LMS, i.e. Google Classroom, etc.). Of course, this phenomenon provides different opportunities and challenges than before. On the one hand, students and lecturers have the flexibility of time and place for online learning. On the other hand, students and lecturers have the flexibility of time and place for learning in the online model. As is commonly the case, graduate students usually already have a job, for example as a teacher, so this opportunity provides convenience for them. However, on the other hand, can online learning provide the same quality as face-to-face learning? This is still questionable because face-to-face learning not only teaches knowledge, but also educational culture, work ethic, discipline and so on. The challenge of using online/blended learning technology is not a problem due to the high digital literacy of lecturers and students.
- Business/industry and community needs: Education has an important role in the development of the Society 5.0 era, namely to advance the quality of human resources. Therefore, education is needed regarding 21st century life skills or better known as 4C (Creativity, Critical Thinking, Communication, Collaboration). In Society 5.0 that will be faced later, not only basic literacy is needed but also other competencies, namely being able to think critically, reason, be creative, be communicative, collaborative, and have problem-solving skills. To face this society 5.0 era, education units also need a change in the education paradigm. Among them, educators minimize their role as learning material providers, educators become inspirers for the growth of students' creativity. Educators act as facilitators, tutors, inspirers and true learners who motivate students to Merdeka Belajar.
- Curricula from national association organizations: Association of Higher Education Informatics and Computer (APTIKOM): In the era of VUCA (volatility, uncertainty, complexity, ambiguity), the world, especially education, is expected to be able to respond to global dynamic conditions innovatively and productively, in order to create an innovation ecosystem to master the global economy. Thus, APTIKOM as an association in the field of Computer Science provides guidance in curriculum preparation and learning implementation. These guidelines also synergize with the Indonesian National Qualifications Framework (KKNI), Computing Curricula 2020, and international professional associations. Based on the Computing Curricula 2020 adopted by APTIKOM, computing education is divided into Software Engineering, Computer Engineering, Information Technology, Cyber-Security, Information System, and related disciplines.
Based on the results of the tracer study, alumni of the Master of Computer Science Education study program have jobs that are in accordance with the designed graduate profile where alumni work as informatics or allied teachers/lecturers/researchers, practitioners in the industrial world in the field of computer science and entrepreneurs who utilize the science of computer science education.
4. Graduate Qualification Profile
Graduates of the MP-CSE possess general competencies encompassing attitudes and values, as well as specialized competencies in knowledge, general skills, and specific skills. These competencies define the graduate profiles as follows:
- Educator: Graduates who are equipped to educate, teach, mentor, guide, train, assess, evaluate, and develop educational processes and learning methodologies.
- Professional: Graduates who are skilled in computer science and education, capable of contributing to industries as programmers, multimedia designers, or networking engineers.
- Entrepreneur: Graduates who leverage their expertise in education and computer science to create innovative solutions.
5. Learning Outcomes
The following are the Learning Outcomes of Master of Computer Science Education:
- Attitude:
- PLO-1 Demonstrate scientific, educative, and religious attitudes and behaviors, which contribute to improving the quality of life in society, nation, and state based on culture, norms, and academic ethics.
- Knowledge:
- PLO-2 Able to integrate concepts and knowledge of technology, pedagogics, content (TPACK) in planning, implementing and evaluating Higher-Order Thinking Skill (HOTS) oriented learning processes.
- PLO-3 Apply theories and techniques of computational thinking, programming algorithms, data analysis, computer networks and the internet, software engineering, and multimedia to face the challenges of the industrial era 4.0 and society 5.0.
- General Skills:
- PLO-4 Able to integrate learning and innovation skills, mastery of technology and information, career development, and life skills to become a lifelong learner.
- PLO-5 Able to develop and publish logical, critical, systematic, and creative thinking through scientific research, creation of designs or works of art with an interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approach, which pay attention to and apply humanities values in accordance with their field of expertise.
- Special Skills:
- PLO-6 Able to adapt pedagogical, professional, social, and personality skills/competencies to a dynamic environment.
- PLO-7 Able to develop literacy, critical thinking, creativity, communication, and collaboration skills (21st century skills) in solving problems using a computer science approach.
6. Curriculum Structure
The curriculum structure of the Master of Computer Science Education program is designed for 4 semesters with a total of 57 credits, consisting of 10 credits of Academic Skills Development (PKA), 39 credits of Expertise Development (PKBI), and 8 Thesis credits. Students from outside the field of Computer Science Education may take alignment courses amounting to 12 credits in the Linearity Development of Study Program Expertise (PLKP). The distribution per semester can be seen in the table below:
| Semester | Total Credits |
|---|---|
| Semester I | 16 Credits |
| Semester II | 16 Credits |
| Semester III | 13 Credits |
| Semester IV | 12 Credits |
| Total | 57 Credits |
Figure dibawah illustrates the Master's Curriculum in Computer Science Education, which spans 4 semesters with a total of 102 ECTS.
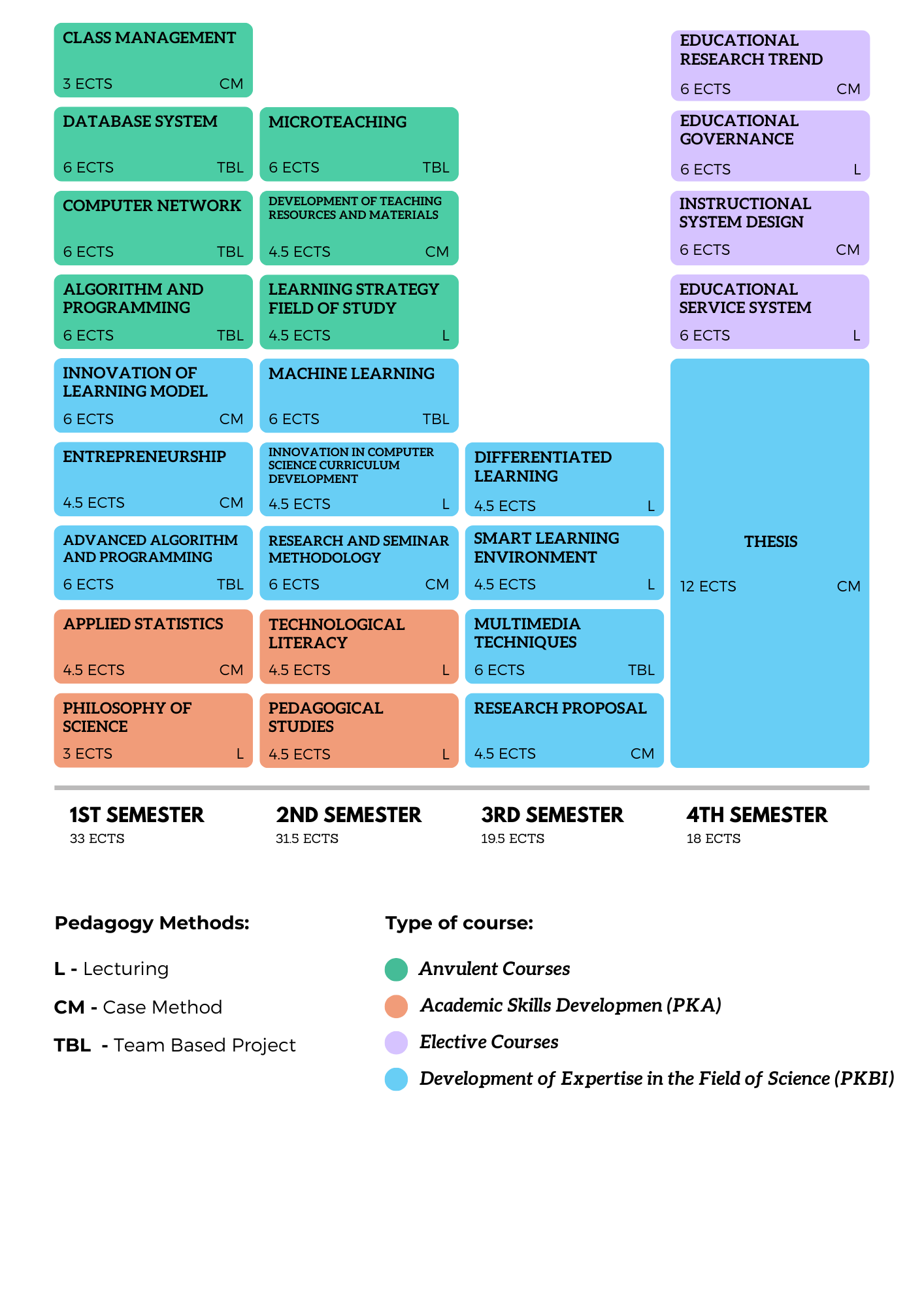
7. List and Distribution of Courses
The following table is a complete list of courses in the Master of Computer Science Education Study Program:
A. Academic Skills Development
| No. | Code | Course Name | Credits | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 3 | Semester 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KA700 | PHILOSOPHY OF SCIENCE | 2 | X | |||
| 2 | KA706 | APPLIED STATISTICS | 3 | X | |||
| 3 | KA701 | PEDAGOGICAL STUDIES | 2 | X | |||
| 4 | KA704 | TECHNOLOGICAL LITERACY | 3 | X | |||
| Total Credits | 10 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | ||
B. Expertise Development
Core Courses
| No. | Code | Course Name | Credits | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 3 | Semester 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IK700 | ADVANCED ALGORITHM AND PROGRAMMING | 4 | X | |||
| 2 | IK710 | ENTREPRENEURSHIP | 3 | X | |||
| 3 | IK720 | INNOVATION OF LEARNING MODEL | 4 | X | |||
| 4 | IK730 | RESEARCH AND SEMINAR METHODOLOGY | 4 | X | |||
| 5 | IK740 | INNOVATION IN COMPUTER SCIENCE CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT | 3 | X | |||
| 6 | IK750 | MACHINE LEARNING | 4 | X | |||
| 7 | IK760 | MULTIMEDIA TECHNIQUES | 4 | X | |||
| 8 | IK770 | SMART LEARNING ENVIRONMENT | 3 | X | |||
| 9 | IK780 | DIFFERENTIATED LEARNING | 3 | X | |||
| 10 | IK701 | EDUCATIONAL SERVICE SYSTEM* | 4 | X | |||
| 11 | IK711 | INSTRUCTIONAL SYSTEM DESIGN* | 4 | ||||
| 12 | IK721 | EDUCATIONAL GOVERNANCE* | 4 | ||||
| 13 | IK731 | EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH TREND* | 4 |
*Choose one course
Thesis and Proposal Courses
| No. | Code | Course Name | Credits | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 3 | Semester 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | KA710 | RESEARCH PROPOSAL | 3 | X | |||
| 2 | KA714 | THESIS | 8 | X |
C. Linearity Development of Study Program Expertise
| No. | Code | Course Name | Credits | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 3 | Semester 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | IK100 | ALGORITHM AND PROGRAMMING | 4 | X | |||
| 2 | IK240 | COMPUTER NETWORK | 4 | X | |||
| 3 | IK210 | DATABASE SYSTEM | 4 | X | |||
| 4 | IK160 | LEARNING STRATEGY FIELD OF STUDY | 4 | X | |||
| 5 | IK412 | DEVELOPMENT OF TEACHING RESOURCES AND MATERIALS | 4 | X | |||
| 6 | IK372 | EVALUATION OF LEARNING FIELDS OF STUDY | 4 | X |
Total Credits: 12 in Semester 1, 12 in Semester 2, 0 in Semester 3, 0 in Semester 4
*Choose three courses
8. Learning Process
The learning process is designed so that it has the characteristics, planning, and implementation of a good learning process and has a well-distributed learning load. The characteristics of the learning process are interactive, holistic, integrative, scientific, contextual, thematic, effective, collaborative, and student-centered. The characteristics of this process are outlined in learning outcomes that reflect the learning process that encourages the formation of a comprehensive and broad mindset by internalizing local and national excellence and wisdom.
The existence of linkages between learning outcomes with each other requires the learning process to be developed thematically, integratively, collaboratively, and contextually in accordance with the demands of the ability to solve problems in the scientific realm of computer science education, with a scientific approach so as to create an academic atmosphere that forms values in accordance with the norms, religion, and national ethics.
The learning process can be carried out in various forms such as lectures, responses, tutorials, seminars, practicums, field practices, and or through school field introduction programs. Learning methods adapt to developments and needs through interactions between lecturers, students, and learning resources in schools, industry, and other environments that are considered effective in achieving learning outcomes.
9. Assessment
Assessment using a standard bias as guidance in assessing the learning process and results in order to achieve the learning outcomes. The principle of assessment refers to learning assessment standards which include educative, authentic, objective, accountable, and transparent principles which are carried out in an integrated manner. The assessment techniques used include written tests, practical tests as well as performance and/or products as student work in the form of comprehensive assignments. Attitude assessment is carried out throughout learning through moral messages and directions related to learning activities, either directly or indirectly and set forth in the appropriate rubric form, while for the assessment of knowledge and skills using one or a combination of the assessment techniques that have been mentioned.
The end result of learning is the integration of established assessment techniques and instruments by upholding the principle of transparency. The mechanism for implementing the assessment is carried out starting from the preparation, implementation, providing feedback, as well as publication and documentation in accordance with the schedule set by the university. Furthermore, the assessment of learning achievement every semester is poured with a semester achievement index.
10. Mapping PLO versus Qualification Profile
| Learning Outcome Code | Learning Outcome | Educator | Professional | Entrepreneur |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLO-1 | Demonstrate scientific, educational, and religious attitudes and behaviors that contribute to improving the quality of life in society, the nation, and the state based on culture, norms, and academic ethics. | √ | √ | √ |
| PLO-2 | Capable of integrating concepts and knowledge of technology, pedagogy, and content (TPACK) in planning, implementing, and evaluating learning processes oriented toward Higher-Order Thinking Skills (HOTS). | √ | √ | |
| PLO-3 | Apply theories and techniques of computational thinking, programming algorithms, data analysis, computer networks and the internet, software engineering, and multimedia to face the challenges of Industry 4.0 and Society 5.0. | √ | √ | √ |
| PLO-4 | Capable of integrating learning and innovation skills, mastery of technology and information, career development, and life skills to become lifelong learners. | √ | √ | |
| PLO-5 | Capable of developing and publishing logical, critical, systematic, and creative thinking through scientific research, design creation, or artistic works with interdisciplinary or multidisciplinary approaches, while considering and applying humanitarian values relevant to their field of expertise. | √ | √ | |
| PLO-6 | Capable of adapting pedagogical, professional, social, and personal skills/competencies to dynamic environments. | √ | √ | √ |
| PLO-7 | Capable of developing 21st-century skills (literacy, critical thinking, creativity, communication, and collaboration) in solving problems using computer science approaches. | √ | √ | √ |
11. Mapping PLO versus Courses
| Course | Credits | PLO-1 | PLO-2 | PLO-3 | PLO-4 | PLO-5 | PLO-6 | PLO-7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Algorithms and Programming | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Entrepreneurship | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Innovation in Learning Models | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Research Methodology and Seminar | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Curriculum Development Innovation in Computer Science | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Machine Learning | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Multimedia Techniques | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Smart Learning Environment | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Differentiated Learning | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Educational Service Systems | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Learning System Design | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Education Governance | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Trends in Educational Research | 4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Research Proposal | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Thesis | 8 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Technology Literacy | 3 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |